Case Study of Mass Timber Construction – GDI Property Group (Australian REIT) 28 November 2022
 <
<
GDI Property Group (GDI), an Australian listed REIT headquartered in New South Wales, Australia, is currently constructing Perth’s first hybrid mass timber and steel frame office building. GDI will utilize a mix of cross laminated timber and steel to construct WS2, an 11 story, 9,500 square meter office building with the goal of creating a best-in-class, sustainably focused asset.
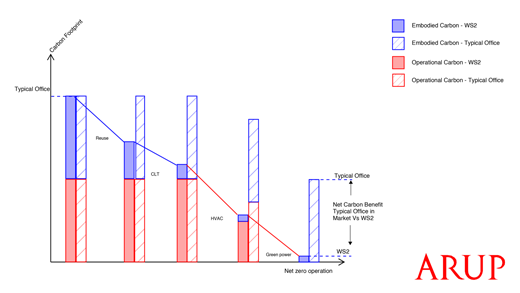
GDI underwent extensive research to understand both the environmental and economic impacts of developing what they’re calling Perth’s most environmentally friendly premium grade office building. Upon completion in late 2022, WS2 will boast a 5-star NABERS Energy Rating, a 5-star Greenstar Rating and will show a reduction of carbon by approximately 50% over the building’s lifespan vs. a similar al concrete/steel-based building and a reduction of 80% embodied carbon during the construction phase. This reduction will be captured through a combination of offsets, renewable energy systems within the building, and significantly lower embodied carbon during the construction phase. Ultimately, the goal is to achieve net zero operation, lowering scope one and two emissions, while achieving a better economic outcome as timber construction is “quicker and cheaper to build on a Total NLA Basis” according to the company in their 10 November presentation.
What Is Mass Timber Construction?
Mass timber, sometimes referred to as Cross Laminated Timber, consists of multiple layers of dried lumber stacked in alternating directions and bound together with structural adhesives and pressed to form a single panel. The panels are specifically engineered to meet the high strength ratings of load bearing walls, floors and roof trusses and are often produced on-site. The resulting mass timber panels are significantly lighter than both concrete and steel (on average 1/5th the weight of steel beams) while maintaining a stronger strength to weight ratio.
Current building codes for mass timber projects vary across different countries, but recent legislation in the United States and Canada has allowed for construction of mass timber buildings up to 18 stories tall. Other markets, such as parts of Europe and Australia, are seeing even more progressive mass timber building requirements with a new 40-story mass timber building in Sydney being designed and scheduled to start construction in 2023.
Building and Environmental Advantages of Mass Timber
Environmental Impact:
- Mass timber decomposes at a natural rate when discarded as opposed to waste from concrete or steel.
- One cubic meter of mass timber sequesters roughly one ton of CO2.
- In a full lifecycle analysis of mass timber vs reinforced concrete on a mid-rise building, mass timber represented a 26% reduction in global warming potential.
- Mass timber construction as an alternative to steel reduces CO2 emissions by 1.9 metric tons per cubic meter of wood product
Tensile Strength: Timber supports its own weight at a higher degree than both steel and concrete.
Electrical & Heat Resistance: Natural resistance to electrical conduction when dried to standard moisture levels. Strength and dimensions are not significantly affected by heat, providing stability to the finished building.
Sound Absorption: Acoustic properties make it ideal for minimizing echo in living or office spaces. Wood absorbs sound, rather than reflecting or amplifying it.
Economic Feasibility of WS2 and Mass Timber Construction
David Ockenden, GDI’s Head of Development, explains the similarly robust economic benefits of the mass timber build due to the expedited construction timeline and relatively light material. Namely, the tensile strength of mass timber allowed for a larger construction footprint than previously thought on the WS2 building:
“When we initially started looking at traditional concrete structures it [could] only be two stories, but timber, when we started exploring that we could build a lot more and reinvest in the precinct to upgrade it.”
The demand for sustainable assets is especially high in Perth, a city known for commodity extraction, where companies are often seeking ways to improve their ESG impacts. GDI is already seeing strong leasing interest from potential full-building, multi-floor and single-floor tenants, claiming overwhelming praise and popularity of the WS2 project. When fully completed, the WS2 building will be a flagship office space within GDI’s portfolio and will serve as the basis for continued mass timber development throughout Western Australia. As mentioned above and in their recent Managing Director’s update, GDI has identified other projects where they plan to use timber construction in their recent update and are exploring redevelopment opportunities at 1 Mill Street and the Wellington car park. Their presentation cites that development approvals have been lodged or are in the process of being lodged.
Benefits of Investing in Mass Timber Projects
At B&I Capital, an Asset Manager with offices in Zurich, Singapore and Austin focused on listed real estate investing, we strive to integrate Environmental, Social, and Governance criteria throughout our investment process and company operations. We believe mass timber construction projects, such as WS2, align directly with our aim to minimize environmental footprint by lowering scope one and two emissions as much as possible. Moreover, given timber construction permitted significant increase in net leasable area and has a quicker construction time, timber construction led to a better economic return. The strong reduction in carbon emissions due to their construction will lower their need to purchase green power or carbon credits to achieve net zero for WS2. Our investment in GDI follows our support of their drive to build environmentally friendly projects and belief of their viability as strong real estate investments. It is through our investments in companies like GDI we actively participate in the creation of a sustainable future.



