The Business Case of Embracing ESG – A CDL Case Study 27 November 2023
2023 is set to be the hottest year since records began in the mid-1800s. The Swiss Re Institute further warns that without climate action, the world economy could shrink by 18% in the next 30 years. Asian economies are particularly vulnerable – with China at risk of losing almost 24% of its GDP under the most severe climate scenario. In contrast, these figures can lessen and be as low as 4% if the 2015 Paris Agreement targets are met.
The cost of inaction is greater than the cost of action. With societal demands for ethical and responsible business practice intensifying, consumers, investors, and employees are increasingly scrutinising companies' ESG (environmental, social and governance) performance, favouring those that prioritise environmental stewardship, social responsibility, and sound governance.
City Developments Limited (CDL)’s ESG strategy and firm commitment to “Conserving as We Construct”, established in 1995, has positioned the company well in the transition towards sustainable business operations. Its value creation business model anchored on four key pillars — Integration, Innovation, Investment, and Impact – provides the company with a solid foundation to mitigate and adapt to unprecedented threats and challenges. With long-standing board and leadership commitment and stakeholders’ support, CDL has remained effective in achieving three deliverables: “Decarbonisation”, “Digitalisation and Innovation” and “Disclosure and Communication”.
Integrating Sustainability into a Company’s Governance Structure, Strategy and Operations
In 2012, CDL established a dedicated Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) and Corporate Governance comprising independent directors, to provide strategic direction and oversight of its ESG activities. In 2016, the committee was renamed Board Sustainability Committee. The committee ensures that ESG considerations are embedded within CDL's corporate strategy and decision-making processes.

CDL’s integrated sustainability governance structure that extends both horizontally between the ESG pillars and functions and vertically across hierarchical levels up to the Group CEO and the Board
Effective corporate governance includes putting in place essential policies and guidelines across the organisation. To enhance transparency, CDL’s corporate policies and guidelines are publicly available on its corporate website, sustainability microsite and staff intranet.
Innovation and Investment: Harnessing Green Technologies and Sustainable Financing
Climate and social risks are business and investment risks. As demand for green financing grows, companies with strong ESG performance will gain better access to fast-growing ESG investment funds. In 2022, CDL established its Sustainable Investment Principles to govern ESG factors in investment decisions, aligning CDL's investments with its commitment towards a low-carbon future.
Building a green and low-carbon future is not possible without smart and innovative solutions. In 2020, CDL set up Green Building, Decarbonisation and Safety team to play a pivotal role in driving innovation and investment. The team identifies and implements cutting-edge technologies and solutions to reduce CDL's carbon footprint in construction, operations, and asset management.
Impact: Setting targets, tracking, and disclosing ESG performance
Companies can only manage what they measure. As the first Singapore company to publish a dedicated sustainability report since 2008, CDL has benefitted from the hands-on experience of producing 16 sustainability reports to-date. Using a unique blended reporting model harmonising key and relevant international reporting frameworks, standards, and approaches with the GRI Standards at its core, CDL has been able to identify material issues, set targets, track performance, and improve deliverables. This has enabled its management to take strategic and prompt action to improve, generate positive impacts and future-proof its business.
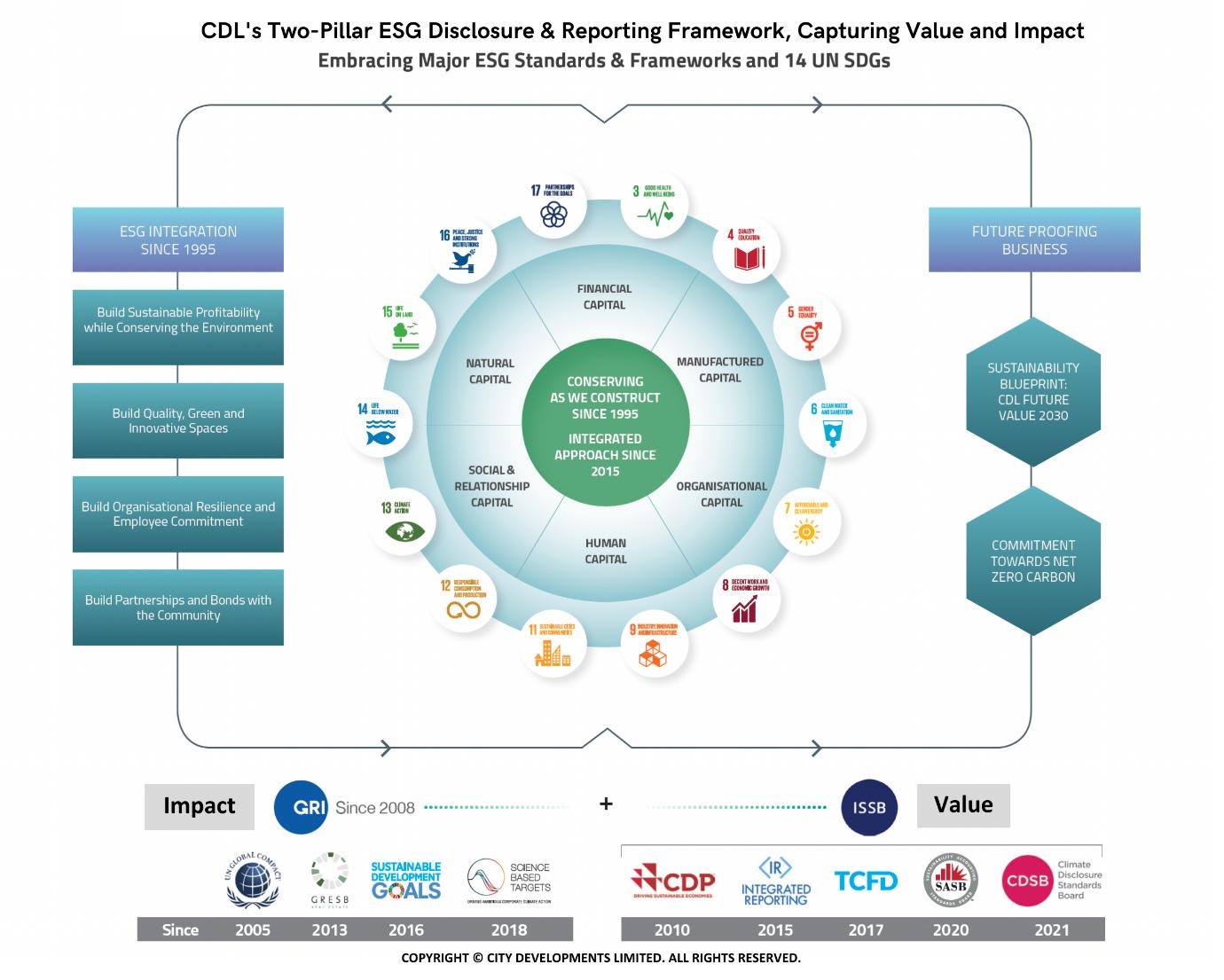
CDL’s Value Creation Model, a unique blended two-pillar sustainability reporting framework that harmonises nine key ESG reporting standards and 14 UN Sustainable Development Goals
Looking ahead, the global race to zero will continue to exert pressure on countries and companies to accelerate climate action. Sustainability-related risks and opportunities will likely increase as social, political, and cultural attitudes continue to evolve. The integration of ESG into a company’s corporate strategy is thus critical for sustained value creation.
1 Analysis: ‘Greater than 99% chance’ 2023 will be hottest year on record | Carbon Brief, Oct 2023
2 Climate change has cost the EU €145 billion in a decade | World Economic Forum, Dec 2022
3 The Paris Agreement is a legally binding international treaty on climate change. It was adopted by 196 Parties at the UN Climate Change Conference (COP21) in Paris, France, on 12 December 2015 and entered into force on 4 November 2016. It aims to keep the increase in the global average temperature to well below 2°C above pre-industrial levels and pursue efforts to limit the temperature increase to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels. | United Nations Climate Change

Esther An
Chief Sustainability Officer
City Developments Limited


